How to Choose the Right Fasteners for Motorsport Applications

- April 30th, 2025
- Categories: Uncategorised
A race car is not built the same as your average production car. Motorsport fasteners make it possible for them to handle extreme conditions such as high speeds, intense vibrations, elevated temperatures, and fluctuating loads, so every component needs to meet incredibly high standards of strength.
The wrong fastener can lead to failures such as component detachment or drivetrain malfunctions, risking both the vehicle and the driver. This blog will be your guide to choosing the most durable options. Engineers cannot afford to make mistakes.
Why Are Motorsport Fasteners Essential?
Let’s take a quick look at why motorsport fasteners are needed:
- They stop components from loosening from vibrations on the track or high-speed impacts
- Every gram counts in racing, and motorsport fasteners make cars lighter
- Engines, exhaust systems and braking components generate extreme heat on the race track, and motorsport fasteners are resistant to high temperatures
- They secure body panels, wings, and undertray to improve aerodynamic stability
- Motorsport teams need fast pitstops and maintenance. Fasteners (such as quick-release) allow for faster assembly
- Offers more customisation; motorsport fasteners are precisely made with specific torque requirements
For instance, suspension systems in race cars endure continuous compressive and tensile forces as they navigate high-speed turns, while engine fasteners must withstand thermal and mechanical stresses from combustion cycles. Whether you’re a trainee engineer or experienced, you must know what to use.
Types of Motorsport Fasteners
Fasteners in motorsport applications are available in various materials, designs, and coatings, but which are commonly used fasteners in the industry?
Nylon Insert Locknuts
Nylon insert locknuts, or Nyloc nuts, are resistant to vibration-induced loosening. The nylon insert creates friction against the bolt threads, preventing self-loosening. These locknuts are excellent in areas subjected to substantial mechanical vibrations, such as suspension and chassis components.
However, it’s important to note that nylon inserts may degrade under high-temperature conditions, making them unsuitable for applications involving elevated heat. Always understand the fastener type you’re using and what you’re using it for.
Titanium Fasteners
With an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, titanium fasteners are ideal for motorsport scenarios where weight reduction is non-negotiable.
Titanium offers excellent corrosion resistance durability and can handle extreme temperatures, so it works well for critical components like engine parts, braking systems, and high-stress joints.
Specialty Automotive Fasteners
Motorsport needs fasteners that surpass conventional automotive standards. Specialty fasteners may include high-grade stainless steel, exotic alloys, and custom-designed bolts for the unique demands of racing.
These fasteners might feature advanced coatings such as zinc-nickel plating, cadmium plating, or proprietary surface treatments that enhance durability and wear resistance.
What about stainless steel? It is also an iron-based alloy, but it contains at least 10.5% chromium, which alters the surface of the fastener and makes it corrosion-resistant. When fasteners are being used outside of the car engine (such as intake manifold bolts), stainless steel fasteners work well.
The majority of fasteners are made from carbon steel. Why? It is affordable and can be tailored to maximise a number of attributes through simple alloy changes. The adjustment of carbon content (and heat treating) makes the fastener more durable. Adding chromium, silicon, copper, manganese, molybdenum, or nickel in tiny amounts alters the capabilities of the fastener and improves its capacity to be heat treated.
Do you work in the field of aerospace and want to grow your knowledge of fasteners and tooling? Read: What are nut plates and what are their uses in aerospace applications?
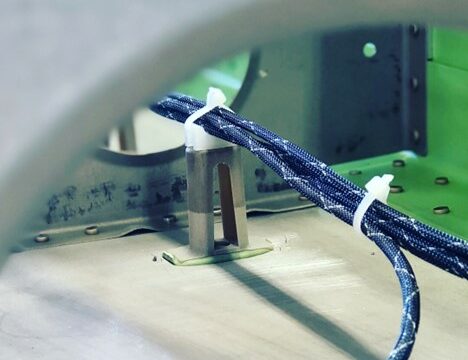
Avibank Ball Lok Pins
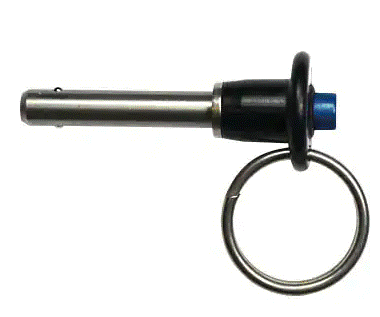
Avibank BLC4BA10S Ball Lok Pin ¼ Inch Diameter with 1 Inch Grip (Stainless Steel)
Avibank Ball Lok Pins is the largest producer of quick-release pins and fastening devices based on locking balls.
- Single Acting Ball Lok Quick Release Pins are positive locks that only require a push of a button to release the balls. Standard and Metric sizes are available.
- Double Acting Ball Lok Quick Release Pins are positive locking and are easy to release as well.
- Detent Ball Lok Release Pins push in and pull out of the application with spring-loaded balls performing the impedance lock.
- Marine Pins are single-acting and made from non-corrosive stainless steel for marine applications.
- Alignment Pins are used on doors, racks, and panel assemblies to align connector contacts, eliminate shear load damage to contacts and door assemblies, and guide them to their proper position.
- Receptacles provide locking for Single-Acting quick-release pins in blind applications when the parent material needs a hardened surface for the balls to lock against. A spring-loaded plunger fills the hole, preventing contamination when the quick-release pin is not engaged. These receptacles can be riveted, threaded, or potted into place.
Dcuz Fasteners
Dcuz fasteners, for example, were developed in the 1930s to secure aircraft panels that needed quick removal for maintenance. This fastener design features a spring-loaded stud encapsulated in a diamond-shaped plate riveted in place on the outer panel.
The spring-loaded stud is compressed to reach through to the receptacle spring riveted to the inner panel/bracket. Rotated through a quarter turn, this locks the stuff to the spring, fastening the two panels together. Now, it is resistant to vibration and accidental release.
Dcuz Sizes
There are two common sizes of Dcuz: the EHF5 type is 37mm across the diamond head end to end and 27mm between the rivet holes.
The larger variant is the EHF6, which measures 44mm from end to end and the rivet spacing is 34mm. With this in mind 90% of applications use the EHF5 size.
Reinforcing backplates are also an option if the use is for lightweight panels; this spreads the load, is especially useful for fibreglass, and mounting brackets for the springs save a lot of fabrication labour.
Camloc Fasteners
With a range of quarter-turn fasteners, Camloc is similar to Dcuz! One of the most popular types is the 2600 Series, which is available as a slot head or crosshead. The receptacle of the 2600 series is a rivet or screw-on type held in place by a locknut. These are selected by the combined panel thickness and start at 0.76mm and go up to 8.37mm.
The 15F Series is a push-button version that doesn’t require tools to operate, only a finger or a thumb, and is a screw-on type only. All variants have a round flange to fit against the outside panel and are secured in place by the retainer washer. 15F suits 0.7mm and 2.33mm depths only.
Rivnuts
Also called a blind rivet, a rivet is a one-piece, internally threaded, tubular rivet that can be anchored entirely to one side, leaving the nut on the inner or lower panel.
Blind rivets can be used on panels, flat-faced tubing, and painted surfaces (since no heat is needed) or to mount components onto a panel or bulkhead.
For example, locking nuts can be used to connect brake rotors to the rotor carriers and reach temperatures of up to 350 degrees Celsius on the track.
Cleco Clamps
Originally used in the aircraft industry (like most fasteners), Cleco clamps are temporary fasteners used to hold components together during assembly or fabrication.
The Cleco clamp fits into drilled holes, holding together with the spring pressure, which is normally compressed with Cleco pliers so the clamp can pass through the workpiece. Releasing the spring load causes the end piece to expand and grip the two workpieces together.
If you are drilling a series of holes in a panel that must align perfectly, Cleco side clamps help the edges on panels to be held.
Each component within a race car serves a specific function, and the corresponding fasteners must have the correct tensile strength, shear strength, and fatigue resistance.
For example, suspension fasteners must endure sudden shock loads without failure, while engine bay fasteners need to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. An assessment of each application’s performance demands means that fasteners will perform under all conditions.
How do these fasteners help with safety and reliability?
Fasteners used in safety-critical applications—such as seat mounts, harness anchors, and roll cages—must comply with stringent regulations and standards. Using industry-standard fasteners with a proven track record in racing environments minimises the risk of failure.
Socket cap head screws, for example, are used for drivetrain mounting, dashboard, floor panels, and aerodynamic devices due to the quick and easy fitment using a standard socket set. Used through the finished car, these fasteners are good for jigging assemblies to keep the chassis and mechanical systems securely in position while being welded or fitted.
Considerations When Choosing Motorsport Fasteners
So, you’ve decided on your material and the type of fastener for the job, but there are still many things to think about before beginning your project in high-stress applications.
Evaluate Bolt Grades
Bolts are categorised into various grades based on material composition and strength. In motorsport, higher-grade bolts, such as Grade 8 (SAE) or 12.9 (ISO), are commonly used for high tensile strength and hardness.
- Grade 2: Low or medium carbon steel with a proof load of 385MPa and a metric size of 5.8. Applications include body hardware, body panels, minor brackets, and seatbelts.
- Grade 5: Medium carbon steel or quenched and tempered, a proof load of 600MPa, and a metric size of 8.8. Applications include key brackets, suspension and steering.
- Grade 8: Medium alloy carbon steel or quenched and tempered, a proof load of 840MPa, a metric size of 10.9, and is applied to torqued engine components and driveline components.
Lower-grade bolts in high-stress scenarios can lead to premature failure and risks on the track. It is important to select the correct bolt grade for safety. Most engineers use a factor of 60% for the strength of the bolt in shear.
Understand Torque Values
Proper torque application is critical in motorsport fasteners to prevent over-tightening or under-tightening, both of which can lead to failure if not careful. Each fastener has a recommended torque specification based on its material and application. Using a calibrated torque wrench cuts the risk of the fastener loosening or breakage.
Some fasteners require preloading, and properly torqued fasteners create a clamping force to keep components secure under intense vibrations and heat cycles.
Review Thread Treatments
Thread treatments such as thread-locking compounds (such as Loctite), dry film lubricants, and anti-seize compounds help improve fastener reliability.
Thread-lockers prevent vibration-induced loosening, while dry film lubricants reduce friction and galling in high-load applications. Anti-seize compounds support high-temperature environments where fasteners are prone to seizing.
Conduct Regular Inspections
Checking for signs of fatigue, corrosion, elongation, or thread damage helps prevent failures before they occur. Regularly re-torquing critical fasteners and replacing worn-out components helps the vehicle to last longer (and needs a lot less repairs) after the track.
In professional racing, teams often implement a strict schedule for fastener inspections so every component is in good working order.
AFT can help you ensure your fasteners and tooling meet the job safety requirements. Here are some tips you should keep in mind:
- Use correctly-sized washers to suit the fastener shank, with a clearance of 0.5 to 1mm. Oversized washers cause issues with clamped or location components.
- Make sure the holes you drill are not oversized for the fastener being used, or looseness, rattling, and slotting can occur.
- For fasteners under 6mm, a 0.5mm clearance is recommended. For a 6-16mm, use 1mm as the clearance hole size.
- Fit spacer tubes or bosses inside hollow items that are being clamped by a fastener. This avoids distortion of the hollow member during torquing or under operational stress.
If you would like to learn more about fasteners, have a read of the benefits of motorsport fasteners and why race cars wouldn’t be the same without them!
Need Motorsport Applications? Order Now From AFT!
Whether you’re in the space, marine, industrial, mining, oil and gas, transport, or motorsport industry, Applied Fasteners and Tooling supplies top-quality products at competitive prices.
Quality-certified and registered in 2014, AFT was founded to supply the aerospace and defence industries with specialised fastening products and technical support.
Contact us today to get a quote and shop in stock! From Click Bond to Hi Lok Tooling and fasteners to Avibank Ball Lock Pins, Nutplate Tooling and Cable Tie Mounts, we offer personalised interactions and a value-added service.