Aerospace and Defence Testing and Approval – Everything You Need To Know

- February 19th, 2024
- Categories: Uncategorised
In the aerospace industry, aerospace and defence testing and approval is critical to the durability and efficiency of fastening and tooling products.
Supporting the development of new products for any given market offers maximum value to customers who rely on durability in extreme temperatures, such as deploying military on missions or building an aircraft strong enough for out-of-space conditions.
Such products are approved for many markets, including defence, marine, mining, space, and electrical and energy. Without putting testing in place, this can be detrimental to these industries.
This article will delve into some of the aerospace and defence testing and approval processes, the types of risk assessments, and how this enhances the defence sector.
Importance of Testing and Approval in the Aerospace and Defence Industries
Why is testing and approving aerospace and defence products so important? There are many reasons that aerospace testing standards must be adhered to.
Safety and reliable products
In the aerospace sector, the stakes couldn’t be higher. Whether it’s the safety of passengers aboard commercial aircraft or the reliability of defence systems crucial for military operations, the utmost quality is non-negotiable. Rigorous testing and strict approval processes are in place to guarantee that these systems excel under extreme conditions, including high altitudes, severe vibrations, intense heat, and other demanding environments.
Compliance with regulatory standards
In the defence and aerospace sectors, stringent regulations govern every aspect of product development and deployment. Government agencies play a pivotal role in ensuring that all products meet rigorous standards before they are deemed fit.
Central to this compliance process is the guarantee of high performance, uncompromising quality, and utmost safety in every aspect of the product’s design, manufacturing, and functionality. This commitment to excellence not only upholds industry standards but also safeguards the lives of those who rely on these critical systems in high-stakes scenarios.
Cost savings
Extensive testing can cost a substantial amount. However, this is an investment for the long term. Resolving issues in the testing phase is more cost-effective than dealing with failures while an aircraft is in operation!
For example, repairs, recalls, and lawsuits resulting from system failures can cost companies millions. If you are unsure if your fastener or tool has gone under significant testing, reach out to a supplier to be put in the right direction.
Maintaining reputation
Defence and aerospace companies must maintain their trust and reputation, especially in government, the military, and the general public. Always ensure products have been thoroughly tested, as a failure concerning public safety can affect long-lasting credibility.
Innovation and advancements
Effective product testing will always drive innovation in the aerospace and defence sectors, pushing engineers forward to explore new techniques and technologies to improve safety. Lessons learned from quality testing procedures advance materials, design, technology, and processes, and this expands to dozens of industries around the globe.
Risk mitigation
As defence and aerospace systems are prone to risk, the risks as the environments in which they operate are to be evaluated. Establishing testing procedures is essential to minimise the chances of failure. These procedures help identify potential issues in advance, allowing for timely corrections and significantly reducing overall risks.
International Standards for Aerospace and Defence Test Management
With product testing and approval for aerospace and defence fields, standards and regulations must be complied with to solidify these systems’ safety, quality, and reliability. With this in mind, what are some of the most important standards?
DO-178C – Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification
With software development in the aviation industry, guidelines are set for software design validation, verification, and quality, so these systems meet rigorous safety and reliability requirements
DO-254 – Design Assurance Guidance in Airborne and Equipment Certification
Focusing on electronic hardware used in airborne systems, this standard guides developing and certifying complex hardware components, such as FBGA-based systems and microprocessors.
AS/EN 9100 – Quality Management Systems for Aerospace
These are a series of standards developed for the aerospace industry. Supporting the development of comprehensive quality management systems covers the development, design, production, servicing, and installation.
ARP4754 – Guidelines for Development of Civil Aircraft and Systems
These guidelines cover the processes and activities for developing civil aircraft and systems, including developing, planning, and validating these systems.
MIL-SPEC – Military Specifications
MIL-SPEC is the standard and requirement for military components and equipment, materials, testing procedures, and quality control.
ISO 9001 – Quality Management System
Although this standard is not simply related to defence and aerospace, the Quality Management System is a foundation for how quality management should work in these industries. Ultimately, this provides a framework for quality assurance in design, development, production, and testing.
Want to learn more about the quality management process? At Applied Fasteners and Tooling, you can meet an experienced supplier of aerospace tools and fastening. Check out the importance of optimising precision and efficiency for countersink tools in defence manufacturing.
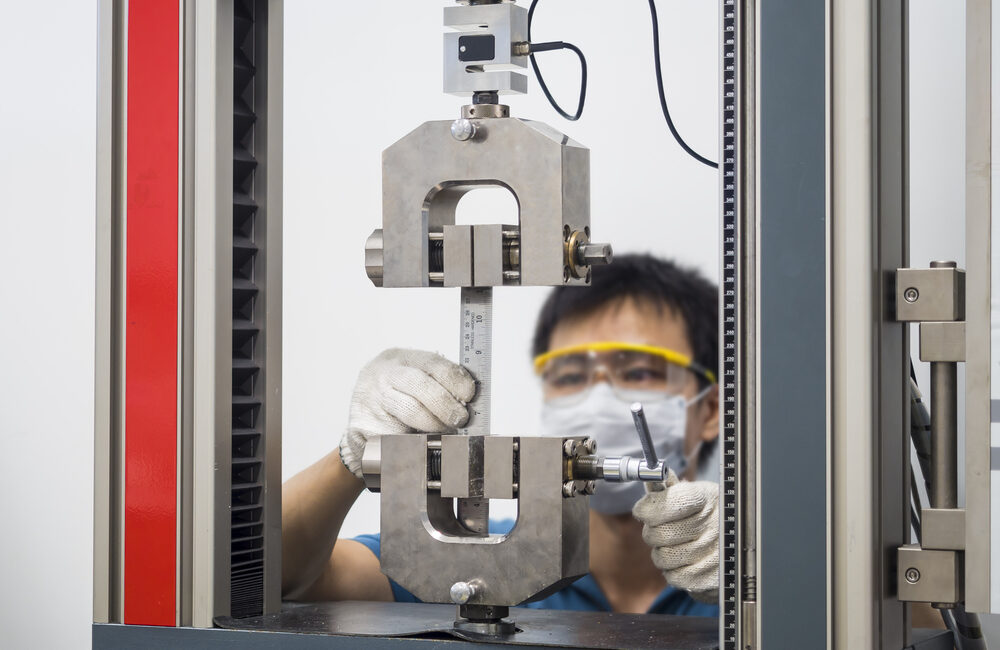
Types of Aerospace and Defence Testing
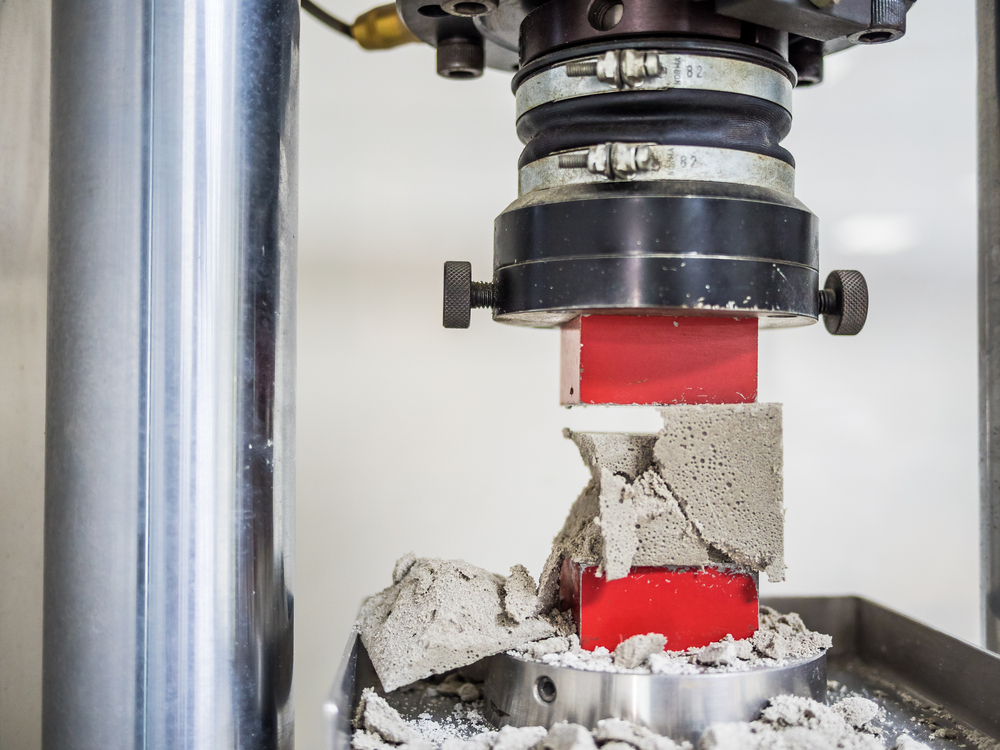

Many testing methods are implemented for product approvals and testing in the defence and aerospace industry. What kinds of testing do fasteners and tooling go through?
- Fatigue testing. In aerospace, fatigue testing is critical for large aircraft. Microscopic to identify, commercial testing determines fatigue life and cracks growth data, identifying important locations susceptible to fatigue. Repeated flight cycles can weaken the metal elements of planes over time.
- Environmental testing. Environmental factors such as extreme heat and cold- can fatigue and degrade components over time. Without testing, noise is created, and vital parts or electrical systems can be displaced—environmental tests with the military show ground materials’ resistance in natural and induced environments.
- Flammability testing. In aerospace, flammability can affect people’s ability to escape. Flammability testing- such as a vertical flame test- determines how fast a material or finished product will burn when exposed to heat. In defence, military shelter materials are tested for the least flammable design.
- Qualification testing. The quality of a product will be evaluated to see if it meets design requirements. Qualification testing also develops information on the integrity of the product, estimates its service life, and evaluates the effectiveness of its materials.
- Susceptibility testing. In aerospace, fluid susceptibility testing is critical to determining whether materials used in equipment can tolerate the damaging effects of fluid contaminants. This could include fuels, lubricating oils, solvents, cleaning fluids, and verifying that the aircraft will operate under all conditions.
Testing and Approval Process – What To Expect
As a structured framework for the planning, executing, and reporting tests for spacecraft, aircraft, defence systems, and related technology, what should you expect from this crucial development process?
1. Test planning
Expect to begin with object definition. This covers defining the end goal of the testing process. What aspects are to be tested?
Next is scope definition. The scope of the testing is outlined, and boundaries are established, covering what will and won’t be included during the product testing.
Thirdly is resource identification. Necessary resources, such as personnel, materials, equipment, or facilities for testing, will be identified and allocated.
Criteria and success metrics are then implemented, defining the conditions for the test to succeed.
Lastly is a test schedule. A detailed schedule is created, planning the sequence and timing for all testing activities.
2. Test design
Test case creation is the first process of test design. These instructions indicate how the testing will be conducted, specifying the steps, data, and expected outcomes.
Next, test scripts or procedures are put into place. This is a written electronic- guide to executing test cases, working as a standardised approach.
Lastly, test data is prepared. Covering inputs and expected results, test data is collected or generated. This is essential for this product testing to be conducted effectively.
3. Test execution
Firstly, a test will be conducted involving the practical execution of the test as per the created plan. This can cover various activities, such as running flight simulations or operating machinery.
Next, real-time monitoring begins. During the test execution, this is employed to observe how these systems behave. Tester can respond immediately to unexpected issues that have deviated from expected results!
4. Test reporting
During product testing, data is collected and recorded. This data could include measurements, observations, and unexpected results.
Next, the data is thoroughly analysed to assess system performance, helping to identify any issues.
Test reports are then generated, documenting the entire testing process, presenting results, and providing helpful insights on product performance.
Lastly, documentation is organised for traceability, and all tests, reports, and test scripts must be well documented for regulatory compliance.
5. Test evaluation and improvement
After product testing, the team conducts a comprehensive review, identifying what went well, what failed, and what lessons were learned during the testing experience.
The lessons learned from these tests encourage process and product improvements. This could include reworking testing procedures, improving documentation, implementing new tools and technologies, and making testing easier in future.
If you’re seeking supplies to support the safety of critical applications that have undergone extensive product testing, Applied Fasteners and Tooling provides Click Bond Fasteners, GripLockTies, Aerospace Tooling, Cherry Tooling, Eddie Bolt Tooling Spares, and more.
Applied Fasteners and Tooling – Choose the Best in Aerospace Tooling
Are you looking for fasteners that meet aerospace and defence testing requirements? At Applied Fasteners and Tooling, we have everything you need for aerospace and industry-standard engineering applications, including Cable Tie Mounts, Hi Lok fasteners, AN fasteners, MS fasteners, Avibank Ball Lock Pins, Adhesives and Equipment and a range of handy tools for your upcoming project.
We supply quality fasteners and assembly tooling consumables worldwide to the space, defence, industrial platforms, marine, transport, and aerospace industries.
Registered and AS9120 Qualified in 2014 by approved standards, we supply the aerospace and defence industries with specialised products and trustworthy technical support. All parts are supplied with certificates of conformance to customer requirements. Meeting the Quality Assurance Procurement Requirements without fail, you don’t need to stress about your design and manufacturing operations with us.