The Role of EMI/RFI Shielding in Modern Avionics

- March 18th, 2025
- Categories: Uncategorised
With digital appliances and radio communication systems being a cause for concern in many industries–especially the aviation sector–EMI disrupts verbal exchange systems, navigation gadgets, and flight controls. Modern aircraft structures depend on these pieces all working together, and without proper shielding, EMI/RFI is incredibly dangerous.
Electromagnetic interference can harm electronics on the ground and avionic equipment 30,000 feet in the air, so being able to defend against this is non-negotiable in the military, defence, and commercial fight industries.
This blog will explore the shielding methods of EMI/RFI, innovations, regulatory requirements, and how you can use EMI/RFI products in your engineering projects.
Definition of EMI and RFI
EMI (electromagnetic interference) shielding is an unwanted disturbance that affects the performance of electronic circuits due to electromagnetic radiation from internal or external sources. Radiofrequency interference (RFI) is the interference of radio frequencies.
Put simply, aircraft are sophisticated networked computing platforms, and it takes critical components to make sure aerospace engineers adopt effective shielding. For example, the modern F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Aircraft, a fifth-generation military combat jet, is five times more complex than the F-16 military aircraft introduced in 1978.
Planes experience interference from human and natural causes, such as:
- Solar flares which are intense bursts of radiation from the sun that disrupt communication systems
- Lightning strikes such as high-voltage surges, can introduce unwanted signals into aircraft electronics
- Radar systems Commercial and military radars emit strong electromagnetic fields that interfere with avionics
- Wiring in the plane which is internal cabling that can generate interference if not shielded
- Personal electronics such as passenger electronic devices
These instances can cause problems such as:
- Corrupted data
- Incorrect flight commands
- Degraded cockpit radios and radar signals
- Interference with air traffic control (ATC) and pilot communications
- Loss of information navigation systems
For example, a passenger’s laptop can cause interference such as displays blanking, flight management computer autopilot, standby altimeter inoperative, and autopilot disconnects.
It is up to plane engineers to protect aircraft and achieve full shielding effectiveness against magnetic fields.
Importance of EMI/RFI Shielding in Avionics

Let’s take a look at why EMI/RFI shielding is so important.
Impact on System Performance
Avionic systems such as communication, navigation and flight control rely on electronic signals that are uninterrupted. Without shielding in place, EMI/RFI degrades these signals, which can lead to malfunctions or complete failures.
Protection of Sensitive Equipment
Modern aircraft are equipped with highly sensitive electronic components, and EMI/RFI shielding helps maintain the reliability and accuracy of these. A proper shield blocks unwanted electromagnetic waves for a stable operation.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
The Federal Aviation Authority (FAA) and the International Civil Aviation Organisation enforce strict regulations on EMI/RFI shielding for flight safety. Compliance with these standards is essential for operational approval and certification.
Shielding Methods in Avionics

What are some of the EMI/RFI shielding methods critical to avionics?
Board-Level Shielding
Board-level shielding is a technique used to protect electronic circuits from electromagnetic interference at the printed circuit board (PCB) level.
This involves enclosing sensitive components such as conductive coatings, metal enclosures, and EMI gaskets to prevent interference between different components within the aircraft’s electronic systems. These shields are made from copper, aluminium, or nickel-plated steel and are either attached using clips or soldered directly onto the PCB.
Board-level shielding can also include the use of ground planes and multilayer PCBs, which provide a controlled environment for signal routing. Shielding at this level is important for high-frequency circuits and densely packed electronic assemblies in avionic systems.
Gasketing Techniques
Conductive gaskets provide a defence against EMI/RFI shielding by sealing the gaps between enclosures, connectors, and access panels. These gaskets are made from metal foils or conductive paints to defend vulnerable electronics from external electromagnetic radiation. There are several types of EMI/RFI shielding gaskets used in avionics:
- Metallic mesh gaskets which are made from woven or knitted mesh, are used in high-performance applications.
- Conductive elastomer gaskets are made from silicone or fluorosilicate with conductive particles such as nickel, silver, or carbon.
- Fabric-over-foam gaskets are a lightweight solution of conductive fabric wrapped around a foam core for flexibility, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness.
- Finger stock gaskets These are made from beryllium copper or other conductive metals. They’re ideal for shielded doors and enclosures.
EMI shielding gaskets are usually installed during the design stages to isolate a certain section of a system from another.
The gaskets are implemented between the mating surface and the shield housing of an electrical system. The great thing about them is they meet a wide range of complicated applications and can be customised for specific roles.
Hybrid Shielding Strategies
Aircraft use a combination of shielding techniques to protect critical applications for flight. Hybrid shielding, in this case, integrates conductive materials, filters, and absorption techniques, such as:
- Multilayer shielding enclosures This means using layered conductive materials to improve absorption and reflection of EMI.
- Integrated filtering circuits This combines passive and active filtering techniques within shielded enclosures to prevent interference within multiple frequency ranges.
- Absorptive shielding materials This means using materials that reflect EMI but also absorb and dissipate electromagnetic waves.
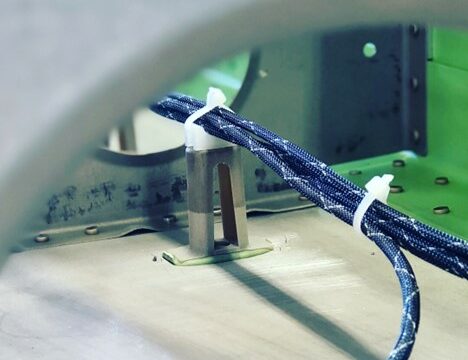
According to an article by ScienceDirect, although there are conventional methods to fabricate EMI shielding materials, electrospinning is highly advantageous over other composite manufacturing processes, resulting in nanofiber with a regulated shape, high surface area, and uniformity.
If you would like to learn more, read about cable management systems for safety in flight!
Innovations in Shielding Technologies

Advanced Materials for Shielding Techniques
Advancements in shielding materials include highly conductive polymers, composite materials, and metallised fabrics that offer lightweight EMI/RFI protection.
Foils: Foils are thin sheets of conductive materials like aluminium or copper that can absorb or block electromagnetic interference. They are flexible, easy to mould, and compatible with a number of surfaces and shapes.
Tapes: Aluminium and copper conductive tapes can shield electronic components from electromagnetic and radio-frequence interference. Tapes are used to cover joints, seams, and gaps to block signals.
Insulators: Rubber, ceramics, and plastics control the flow of electricity, so they can block unwanted signals! Highly resistant to electrical currents, insulators prevent short circuits.
Are you in need of specific fasteners and tooling for your project? AFT offers Hi Lok tooling, countersink tooling, Dotco tooling, Eddie Bolt tools, hand tools, rivet tooling, and so much more.
Nano-Enhanced Shielding Solutions
Nanotechnology has introduced materials with enhanced electromagnetic shielding properties. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs), graphene-based coatings, and metal nanoparticle-infused materials offer superior protection while still being lightweight.
- Carbon nanotubes which offer thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
- Metal nanoparticle-infused materials are embedded with silver, copper, or aluminium nanoparticles.
- Graphene-based coatings are made from graphene, which is a single layer of carbon atoms and can be applied as a thin coating on electronic enclosures.
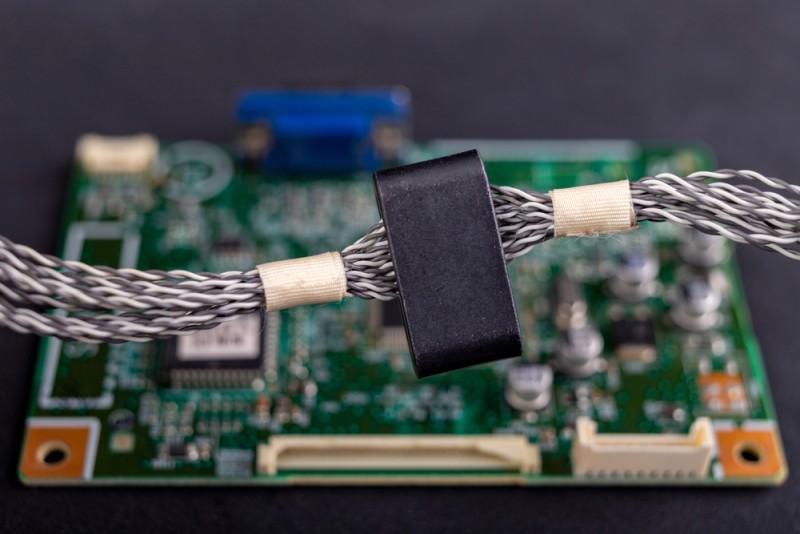
To achieve full shielding (harnesses, enclosures, and connectors), engineers must:
- Choose the correct enclosure materials
- Design sealing gaskets
- Created a PCB design and layout that is effective
- Choose the correct conductive mating surfaces
- Properly terminate all cable shields
Regulatory Requirements for EMI/RFI Shielding
International Standards
Organisations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics (RTCA) establish global standards for EMI/RFI protection. Compliance with these standards ensures the safety of avionic systems across the globe.
Industry-Specific Guidelines
Commercial, military and private aviation sectors have their own specific EMI/RFI shielding requirements.
For example, MIL-STD-461 outlines the electromagnetic compatibility standards for military aircraft, whereas DO-160 governs the environmental conditions for airborne equipment in commercial aviation.
If you would like an in-depth guide to EMI/RFI shielding, here’s a blog about understanding the basics of EMI/RFI shielding, how it works, and why it matters.
Radar Absorbing Material Suppliers: Choose AFT for Aerospace Tooling!
Whether your project needs positive feed drills, spacecraft fasteners, marine bonded fasteners, Click Bond fasteners, Cable Tie Mounts, GripLockTies, aerospace consumables, or Duocel metal ceramic foam, Applied Fasteners and Tooling have everything you need.
Registered as AS9120 quality certified in 2014, AFT was founded to supply the aerospace and defence industries with specialised fastening products and technical support. Emerging as a leader in the fastening supply chain, we align ourselves with the most innovative fastener-related technologies and companies that push the boundaries of what is possible.
Contact us today for a personalised interaction, a value-added service, responsiveness, and collaboration. Shop in stock and get a quote for custom product solutions in a range of markets!