A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Aerospace Consumables
- November 15th, 2024
- Categories: Uncategorised
You may have read NASA’s Guide to Aerodynamics, but what are the consumables that make these aircraft possible for both private and commercial aircraft owners?
From rotatable parts to general aircraft parts, procurement, and logistics, there are various classifications of parts in aircraft maintenance cycles., In aviation maintenance, expendable aircraft parts are critical, making up many of the replacement parts used in aircraft repair, such as gaskets, seals, bolts, washers, and assorted hardware.
Any aircraft part is disposed of after use rather than rebuilt, and these expendable parts can be very important to a military aircraft maintenance mission.
This blog will be your ultimate guide to aerospace consumables and why they are critical to flight operations.
What Are Aerospace Consumables?

What are the definitions and different classifications of expendable and consumable parts? Let’s look at the primary or core types of expendable parts that are common to aircraft!
Consumable Parts
Here are the most common consumable part categories:
> Gaskets and seals: These are an entirely different category and are replaced routinely throughout all phases of maintenance. Every time a pump is removed or replaced for example, the gaskets have to be replaced!
> Lubricants and oils: All hydraulic fluids, greases, bombers, some fighters, and cooling oils.
> Chemicals: These are used all over an aircraft and commonly include sealants, adhesives, and de-icers.
> O-rings and washers: Although these are small in size, they are important. For example, the average military aircraft uses hundreds–if not thousands–of O-rings and washers to seal parts. They are often used on drain plugs or accessory gear drive boxes, hydraulic pumps, and fluid filters, also known as Delta-Ps.
Fasteners
As one of the most critical expendable parts in the supply system, fasteners are critical to the overall airframe and individual aviation components. Most commonly, these components will be:
> Nuts and rivets: Although they aren’t identical, the same rules apply. Nuts can become corroded and stripped out, so it is a good practice to replace them when removed for maintenance or repairs. As for rivets, they are a one-time-use consumable and are used in all aviation applications. Always have a good stock of rivets!
> Bolts and screws: It is extremely common for fasteners to need replacing during all phases of maintenance as the heads can get rounded, stripped, and the threads easily crossed. Replacing these is inexpensive insurance.
> Pins and clips: As some of the most simple and basic maintenance materials commonly used, clips and pins are used all over the aircraft to secure fasteners. For example, castle nuts are where a nut is not held by a high torque value but instead loose and held in place with a pin. Pins must be discarded after one use, so they need to be part of your bench stock.
Filters
Filters are a category of consumables essential for many areas of an aircraft, especially hydraulic systems and power plants. These filters are replaced as standard intervals for different primary components.
For example, hydraulic systems use filters to extend the life of components and the fluid. APUs and engines are heavily reliant on consumable filters to maintain their reliability, and filters are twice as inexpensive. After all, contaminated or dirty oil is a fast way to destroy a million dollar engine short of FODing it.
Consumables: The Life Cycle of Expendable Parts
When it comes to the standard servicing of both aircraft and component materials, the anticipated lifecycle of expendable parts plays a major role. After all, every fuse, light bulb, relay, and switches are consumable parts.
The lifecycle of expendables varies widely as it depends on the application area of the aircraft from which the consumables come.
Tyres have a general life expectancy between 300 and 500 landings. However, this varies as asphalt runways and Portland Concrete Cement (PCC) runways have substantially different wear characteristics. Predominantly coral runways found in the Pacific increase these wear rates.
Likewise, brake pads are similar and have anywhere between 500 to 2000 braking cycles, although this is impossible to predict. This is why repairs and maintenance are so important.
For flight safety, brake wear indications are checked every through-flight, post-flight, and pre-flight inspection. Brake wear can depend on the tendencies of the pilot, whether the aircraft has thrust-reversing capabilities or a drag chute, and runway length.
How can you manage expendable parts?
Many of these parts are kept in bench stock, although not exclusively due to their high consumption and common demand.
This doesn’t apply to larger consumables like brakes, tyres, and batteries, but hardware, fuses, gaskets, adhesives, and sealants are routinely kept in bench stock for easy access! Tiny parts have a bigger impact than you can imagine, so missing a gasket or O-ring will read X an aircraft straight away.
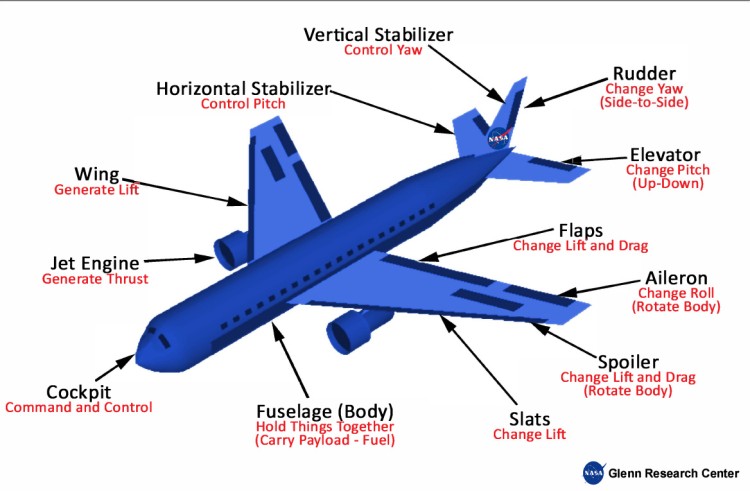
Aircraft Parts and Function
What do aircraft consumables support? Let’s have a quick look.
The Vertical and Horizontal Stabiliser
Smaller wings are located at the tail of the plane to control and manoeuvre the aircraft, and this tail often has a fixed horizontal piece and a fixed vertical piece. The role of the stabiliser is to provide stability for the aircraft and keep it flying straight.
The vertical stabiliser keeps the nose from swinging side to side, whereas the horizontal stabiliser prevents an up-and-down motion of the nose, called a pitch.
Flaps and Spoiler
The wings of the aircraft have additional hinged rear sections near the body called flaps. These are deployed downward on take-off and landing to increase the amount of force produced by the wing.
Slats are used at take-off and landing to produce additional force, and the spoilers are also used during landing to slow down the plane, counteracting the flaps when the aircraft is grounded.
Fuselage
Also called the body of the aeroplane, the fuselage holds all the pieces together. Pilots sit in the cockpit at the front of the fuselage, and passengers and cargo are carried in the rear of the fuselage.
Some aircraft can carry fuel in the fuselage, whereas others carry the fuel in the wings.
Types of Aerospace Consumables at AFT
Whether your project is a military aircraft or a commercial plane, there is a wide variety of consumables available at Applied Fasteners and Tooling. Here are some of the most notable:
Countersink Tooling

Including specialty countersink tooling for thin sheet metal and composite material stack ups, countersink tooling is excellent and includes high speed steel, carbide, and diamond tooling.
When working with titanium and other tough or abrasive materials, 2- and 3- 3-flute carbide tools can require the use of polycrystalline-diamond (PCD) cutting edges. What are some of the features of countersinking tools?
- Can cut carbon composites
- Cut Kevlar or aramid and aluminium
- It can be available in 1, 2 or 3 flutes
- Interchangeable cutter heads for flexibility
- Come with various cutting angles such as 82 degrees, 90 degrees, or 100 degrees to match the specifications of fasteners
- Uses deburring features for a cleaner finish around fasteners, reducing the risk of stress concentration
- Optimised geometry for reducing forces to avoid delamination
- Integrated pilot guide to centre hole
Nutplate Tooling

From hand tools to pneumatic spacematic drills for use on high-accuracy applications in aircraft structures and sheet metal, what are some of the features of nut plate tooling in aerospace? Let’s look at spacematic drill features:
- It can feature 7 or 10 spindle speed selections and more
- Some models are adjustable and have interchangeable foot designs
- The Nutplate drill drills two rivet holes in a 4-second operation, easily convertible to accommodate rivet hole spacing
- High-precision, self-collecting, and automatic, capable of close-tolerance and reaming operations
- Ultra-light for the user and is an ergonomic design
If you would like to learn more about aircraft components and how they are put together, have a read of understanding the different types of aerospace drills!
Rivnut Tooling

Including hand tooling and pneumatic tooling for aerospace fasteners, let’s look at some of the features of rivnut tooling:
- It includes a quick-change mechanism to easily swap different insert types and sizes
- Rivnut tools have alignment guides for accurate insertion and consistent results
- Can set alloy and steel rivnuts in sizes 4mm/5mm/6mm/8mm/10mm
- Can combine air hydraulic flaring and manual unwinding, setting your nutsert/rivnut without high air consumption
- Provides a consistent insertion depth and deformation for a reliable fastener performance
Hi Lok Tooling

When high-tensile strength is needed for extreme applications, Hi Lok can take engineering work to new heights. What are some of their features for aerospace projects?
- Creates a consistent torque on each fastener installed through integrated functions
- One-handed operation, which makes it easier in awkward positions
- Suitable for fastening composite materials
- Hi Lok tooling can be pre-loaded to provide constant clamping force for enhanced joint integrity
- Reduces weight without compromising on aircraft strength
- Replaces damaged fasteners or during maintenance activities for fast repairs
If you work in the aerospace industry in aerospace engineering, consumables are key to flight mechanics.
No matter your project goal, AFT is a reputable supplier with a deep understanding of the markets–from aerospace to military and defence–customer satisfaction and aims for continuous improvement for industries that rely on heavy-duty solutions for safety and regulatory compliance.
Order Consumables at Applied Fasteners and Tooling
Registered and AS9120 quality certified in 2017, Applied Fasteners and Tooling was founded to supply the aerospace and defence industries with specialised fastening products and technical support.
Emerging as a leader in innovation for the fastening system supply chain, we offer a personalised interaction and added-value service through the product life cycle, working with design, procurement, production, quality, maintenance and repair.
Whether your operations require GripLockTies, MS Fasteners, Click Bond Fasteners, Clecos and Temporary Fasteners, Cherry Tooling, Eddie Bolt Tooling or Hi Lok Tooling, AFT meets the Quality Assurance Procurement Requirements for aerospace and aviation engineers requiring the best for maintenance and repairs. Customers depend on us as a reliable partner known for responsiveness, collaboration, flexibility, and on-time delivery.
Contact us today for services such as application engineering support, product development and training, product testing, program management VMI, and more.